What Is the Primary Function of Dna in Organisms
The primary function of DNA is to tell organelles within cells to make protein. DNA is necessary for the production of proteins the regulation metabolism and reproduction of the cell.

Biology Cell Worksheets Biology Worksheet Biology Notes Cells Worksheet
It provides the information for what proteins a cell will make.

. The structure of DNA can be understood in three stages. DNA is a molecule that contains the instructions an organism needs to develop live and reproduce. Nuclear DNA is the DNA contained within the nucleus of every cell in a eukaryotic organism.
DNA serves two important cellular functions. The main function of DNA or Deoxyribonucleic Acid is to contain the genetic information of a living being said genetic information is nothing more and nothing less than therecipeof all physical and structural characteristics of the organism. It is used as the primary energy source for cellular reactions that require an energy input.
For an organism to grow and function properly cells must constantly divide to produce new cells to replace old worn-out. What is the primary function of DNA in organisms. What is the primary function of DNA.
DNA molecules are broken apart inside the cell and the pieces are assembled into proteins. The primary function to DNA is to store and transmit genetic information What is the primary function of DNA in cells. To carry out these functions DNA sequences must be converted into messages that can be used to produce proteins which are the complex molecules that do most of the work in our bodies.
DNA molecules are the building blocks of tissues and carry out the work of each cell. These rules are found inside every cell and are passed down from parents to their children. Each new strand of.
The double Helix unzips and new nitrogen bases are added to create a new strand of DNA to create a new cell. To carry out these functions DNA sequences must be converted into messages that can be used to produce proteins which are the complex. Large compressed DNA molecules with associated proteins called chromatin are mostly present inside the nucleus.
Transports amino acids to the ribosomes. DNA replication requires the nucleotide precursors in the form of triphosphates and a number of proteins and enzymes of which the most important is DNA-polymerase. Holds genetic codeinfo genes and instructions for making proteins.
DNA molecules deliver the pieces of proteins to the site of protein assembly in the cell. DNA contains the basic road map for how an organism will grow and develop. Apart from being responsible for the inheritance of genetic information in all living beings DNA also plays a crucial role in the production of proteins.
It is the building block of life. Looking at the structure of DNA there is a sugar-phosphate backbone that holds the. Up to 24 cash back Functions of living organisms This chart represents the different organelles including their description and function.
Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA is a biological macromolecule that carries hereditary information in many organisms. The double-helix DNA model. DNA contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop survive and reproduce.
Binds to specific active sites. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms including catalysing metabolic reactions DNA replication responding to stimuli providing structure to cells and organisms and transporting molecules from one location to another. Without such packaging DNA molecules would be too long to fit inside cells.
It is embedded in the membranes of cells to aid in transporting materials in and out of cells. A DNA Molecule Consists of Two Complementary Chains of Nucleotides. A DNA molecule consists of two long polynucleotide chains composed of four types of nucleotide subunits.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells are the 2 main types of cells the difference is Prokaryotic cells do not contain a nucleus or membrane bound organelles while Eukaryotic cells do. Each of these chains is known as a DNA chain or a DNA strandHydrogen bonds between the base portions of the nucleotides hold the two chains together As we saw in Chapter 2 Panel 2-6. For example if all of the DNA molecules in a single human cell were unwound from their histones and placed end-to-end they would stretch 6 feet.
The sketch shows a rynchosaur an extinct animal that is known only from fossils. DNA contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop survive and reproduce. There has been much debate about the classification of these creatures.
It is the genetic material passed from parent to offspring and it serves as the information to direct and regulate the construction of the proteins necessary for the cell to perform all of its functions. In the eukaryotic organisms the genetic material is organized into well-defined chromosomes which also replicate by the semi-conservative mechanism. What is the main function of DNA in all organisms.
Chromosomes contain the DNA which is not only responsible for the observed traits or phenotype of an individual but also for processes such as gene regulation protein synthesis and cellular. The primary function of DNA is to hold the genes of the organism. What is the process of DNA replication.
What is the main function of DNA. The primary function of DNA in cells is to be able to reproduce itself. A primary function of RNA is to translate the DNA into the protein structure of every new cell.
Enzymes known as RNA polymerase transcribe DNA into RNA. The chemical structure of DNA the smallest building blocks. Some scientists suggest that they belong with primitive amphibians and some think they are related to snakes and lizardsthe data equally support both cases.
Which statement best explains how to draw a. What is the primary function of DNA in organisms.

Dna Genes And Chromosomes 10 B1 16th April 2007 Genetic Information Chromosome Dna Molecule
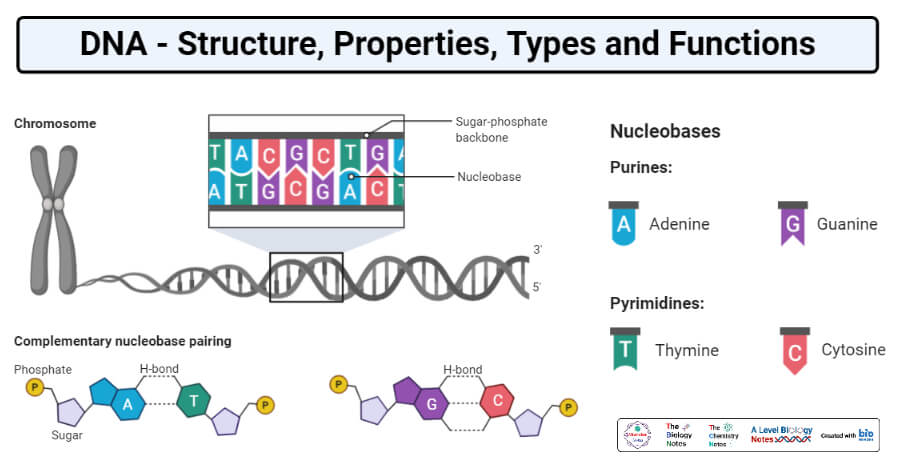
Dna Structure Properties Types Forms Functions

Dna Protein Synthesis Protein Synthesis Dna Replication Prokaryotes

Single Stranded Binding Protein Ssbp Csir Net Life Sciences Dna Replication Dna Human Anatomy And Physiology

Genomes Of Complex Organisms Encode An Abundance And Diversity Of Long Noncoding Rnas Lncrnas That A Gene Expression Structure And Function Molecular Biology

Where Are Your Dna Chromosomes And Genes Diagram Genetics Activities Chromosome Punnett Square Activity

Difference Between Protists And Fungi Characteristics Classification Types Examples Study Biology Protists Biology Notes

Dna Replication Learning Objectives Genetic Information Dna Dna Replication

Genetic Engineering Info Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Cell Structure

Dna Definition Function Structure And Discovery Biology Dictionary

Functions Of Dna Dna Must Do Three Important Things 1 Carry Information From One Generation To The Next 2 Put That Information To Work Determine Ppt Download

Cell Study Guide Biology 101 Free Biology Study Guides Biology Lessons Study Biology Teaching Biology

Question Video Defining The Function Of Chromosomes Nagwa

Difference Between Genetics And Epigenetics Definition Fields Role And Difference Epigenetics Science Biology Genetics





Comments
Post a Comment